Why Choose Graphite Crucibles for High-Temperature Applications?
Summary:
Why Choose Graphite Crucibles for High-Temperature Applications?
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Graphite Crucibles
2. Unique Properties of Graphite
3. Advantages of Graphite Crucibles in High-Temperature Applications
4. Applications of Graphite Crucibles
5. Comparison with Other Materials
6. How to Choose the Right Graphite Crucible
7. Maintenance and Care of Graphite Crucible
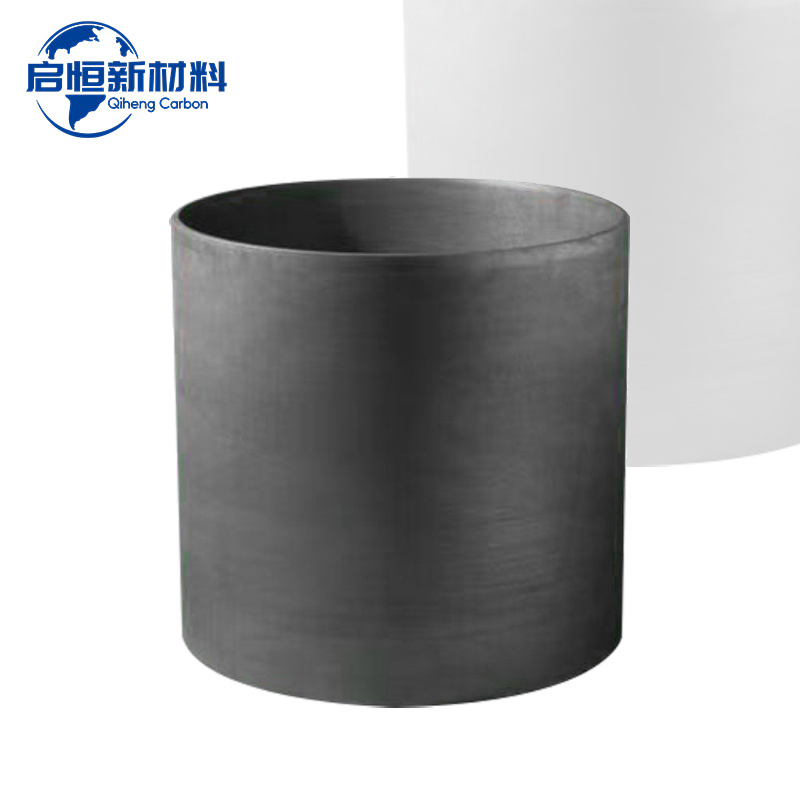
Why Choose Graphite Crucibles for High-Temperature Applications?
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Graphite Crucibles
- 2. Unique Properties of Graphite
- 3. Advantages of Graphite Crucibles in High-Temperature Applications
- 4. Applications of Graphite Crucibles
- 5. Comparison with Other Materials
- 6. How to Choose the Right Graphite Crucible
- 7. Maintenance and Care of Graphite Crucibles
- 8. FAQs about Graphite Crucibles
- 9. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Graphite Crucibles
Graphite crucibles have long been recognized as essential tools in various industries due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures. They are particularly useful in metallurgical applications, where high heat resistance and chemical stability are crucial. These crucibles are made from high-purity graphite, which enables them to perform exceptionally well even under challenging conditions.
2. Unique Properties of Graphite
Graphite possesses several unique properties that make it an ideal material for crucibles:
High Thermal Conductivity
Graphite's thermal conductivity allows for even heat distribution, reducing the risk of thermal shock. This property is essential for high-temperature applications, as it ensures that the material can handle the intense heat without cracking or warping.
High Melting Point
With a melting point that exceeds 3,600 °C (6,500 °F), graphite crucibles can accommodate a wide range of materials, including metals and ceramics that require extremely high temperatures for melting.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
Graphite has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which means it will not expand or contract significantly with temperature changes. This stability is vital for high-temperature applications, where sudden changes in temperature could otherwise lead to material failure.
Corrosion Resistance
Graphite is inherently resistant to corrosion from many chemicals and molten metals. This feature ensures that the crucible maintains its integrity even when exposed to aggressive substances during use.
3. Advantages of Graphite Crucibles in High-Temperature Applications
The advantages of using graphite crucibles for high-temperature applications are plentiful:
Durability and Longevity
Graphite crucibles are designed to withstand the rigors of high-temperature processes. Their durability translates to a longer service life and reduced replacement costs, making them a cost-effective solution for industries.
Versatility
These crucibles can be used for various purposes, including metal casting, glass melting, and even in laboratory settings for materials testing. This versatility makes them a valuable addition to any high-temperature application.
Excellent Thermal Stability
Graphite crucibles maintain their structural integrity at high temperatures, ensuring consistent performance. This thermal stability is crucial for maintaining the quality of the materials being processed.
Easy to Fabricate
Graphite can easily be molded and shaped into different forms, allowing for custom designs tailored to specific industrial needs. This feature is particularly beneficial for businesses that require specialized crucibles for particular applications.
4. Applications of Graphite Crucibles
Graphite crucibles are utilized across various industries, including:
Metallurgy
In metallurgy, graphite crucibles are commonly used for melting ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Their high melting point and chemical resistance make them ideal for processing materials like gold, silver, and aluminum.
Ceramics
In the ceramics industry, graphite crucibles are employed for melting and sintering ceramic materials, ensuring that the high temperatures required for these processes are met without compromising the crucible’s integrity.
Glass Manufacturing
Glass manufacturers use graphite crucibles for melting glass due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist chemical reactions with molten glass.
Laboratory Applications
In laboratories, graphite crucibles are used for high-temperature experiments that require precise temperature control and stability, making them essential for scientific research and development.
5. Comparison with Other Materials
When evaluating crucibles for high-temperature applications, it is essential to consider how graphite compares with other materials such as ceramic, metal, and silicon carbide:
Graphite vs. Ceramic
Ceramic crucibles can be brittle and may crack under thermal shock. In contrast, graphite crucibles are more resilient, offering superior performance in applications that involve sudden temperature changes.
Graphite vs. Metal
While metal crucibles can provide good thermal conductivity, they often suffer from oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures. Graphite crucibles, on the other hand, remain stable and resistant to these issues.
Graphite vs. Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide crucibles can handle high temperatures but may not offer the same level of thermal conductivity as graphite. Graphite crucibles typically outperform silicon carbide in applications where heat distribution is critical.
6. How to Choose the Right Graphite Crucible
Selecting the appropriate graphite crucible for your application involves considering several factors:
Temperature Requirements
Evaluate the maximum temperature your application will reach to ensure the crucible can handle it without degrading.
Material Compatibility
Ensure that the crucible material is compatible with the substances you will be melting or processing. Graphite is a versatile choice, but specific applications may require unique formulations.
Size and Shape
Select a crucible size and shape that fits your melting needs. Custom shapes may be available for specialized applications.
Purity of Graphite
The purity of the graphite used in the crucible can affect the quality of the melted material. Higher purity levels typically lead to better performance.
7. Maintenance and Care of Graphite Crucibles
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your graphite crucibles:
Regular Inspection
Conduct regular inspections for any signs of wear or damage. Early detection of issues can prevent further deterioration.
Cleaning
Clean crucibles after each use to remove any residue. This practice helps maintain the integrity of the material and ensures better performance in subsequent uses.
Storage
Store graphite crucibles in a dry, cool environment to prevent moisture absorption, which can lead to degradation.
8. FAQs about Graphite Crucibles
What is the maximum temperature a graphite crucible can withstand?
Graphite crucibles can withstand temperatures up to 3,600 °C (6,500 °F), making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Can graphite crucibles be reused?
Yes, graphite crucibles can be reused multiple times with proper care and maintenance, although their lifespan may vary depending on the application.
Are graphite crucibles safe to use?
When used correctly, graphite crucibles are safe. However, handling high temperatures requires standard safety precautions.
How do I clean a graphite crucible?
Clean the crucible after use with a soft brush or cloth to remove residue. Avoid using abrasive materials that can scratch the surface.
Where can I purchase high-quality graphite crucibles?
High-quality graphite crucibles can be purchased from specialized suppliers, industrial equipment retailers, or manufacturers that focus on metallurgical products.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, graphite crucibles offer numerous advantages for high-temperature applications, including exceptional thermal stability, durability, and versatility. Their unique properties make them an indispensable tool in metallurgy, ceramics, glass manufacturing, and laboratory settings. By understanding the benefits and selecting the right crucible, industries can optimize their processes and achieve superior results. As the demand for high-performance materials continues to grow, graphite crucibles will remain a top choice for professionals across various sectors.
Previous:
Focus On Hot Spots
RP Graphite Electrodes: Transforming Conductivity in Metallurgical Processes
RP Graphite Electrodes: Enhancing Conductivity in Metallurgical Applications
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to RP Graphite Electrodes
2. Understanding Graphite and Its Properties
3. The Role of RP Graphite Electrodes in Metallurgy
4. Benefits of Using RP Graphite Electrodes
5. The Manufacturing Process of RP Graphite Electrodes
6. Applications of RP Graphite Electrodes
The Essential Guide to Graphite Blocks in Metallurgy and Energy Industries
Graphite blocks are pivotal materials in the metallurgy and energy industries, particularly within the non-metallic mineral products sector. These blocks, made from natural or synthetic graphite, possess unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. One of the most notable characteristics of graphite is its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. This property









