Unlocking the Potential of Graphite Electrodes in Steel Making
Summary:
Graphite electrodes are critical components in the electric arc furnace (EAF) process, which is increasingly favored for steel production due to its energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. These electrodes serve as conduits for electric current, generating the necessary heat to melt scrap steel and produce high-quality steel products. Their unique properties make graphite electrodes th
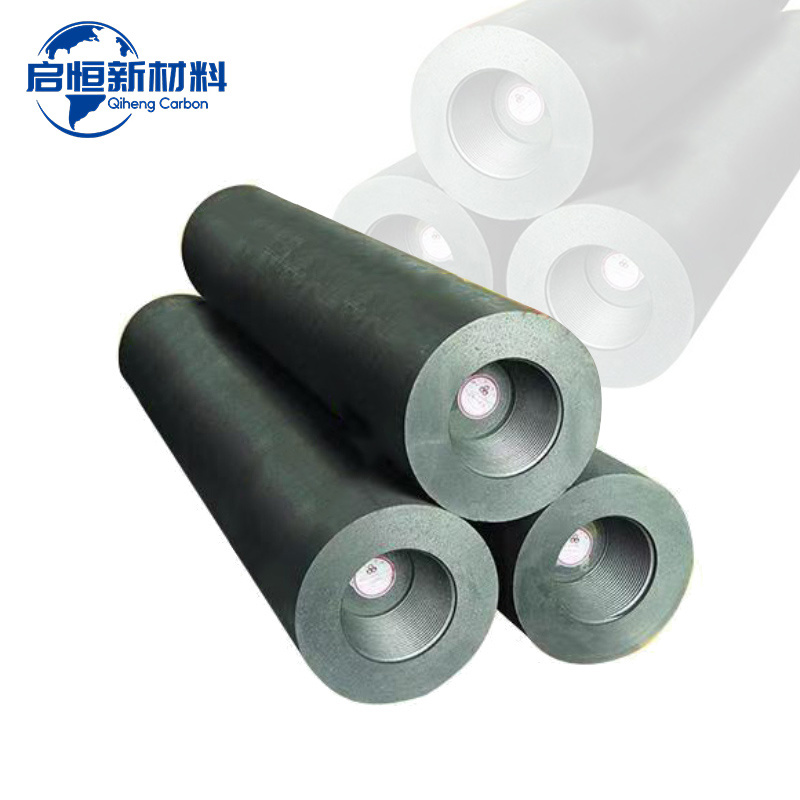
Graphite electrodes are critical components in the electric arc furnace (EAF) process, which is increasingly favored for steel production due to its energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. These electrodes serve as conduits for electric current, generating the necessary heat to melt scrap steel and produce high-quality steel products. Their unique properties make graphite electrodes the material of choice in this demanding application.
One of the primary advantages of graphite electrodes is their high thermal and electrical conductivity. This allows them to effectively transfer electrical energy to the charge in the furnace, facilitating efficient melting. Additionally, graphite has a high melting point, which enables it to withstand the intense heat generated during the steel-making process without degrading. This durability results in longer operational life and reduced frequency of electrode replacement, making the overall process more cost-effective.
Moreover, the purity and quality of the graphite used in the production of these electrodes are crucial. High-quality graphite electrodes are made from premium petroleum coke and are often baked and graphitized at high temperatures to enhance their properties. This ensures that the electrodes maintain their performance under the extreme conditions of an electric arc furnace. When selecting graphite electrodes for steel making, it is essential to consider factors such as the electrode diameter, length, and density, as these characteristics significantly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of the steel-making process.
Additionally, the use of graphite electrodes has evolved with advancements in technology. Innovations such as the use of ultra-high-power (UHP) graphite electrodes allow for higher current densities and improved melting capabilities, which is particularly beneficial in operations aiming for higher production rates. Furthermore, as the industry moves toward sustainability, research is being conducted to improve the recycling and reusability of graphite electrodes, thus minimizing waste.
In conclusion, graphite electrodes are indispensable in the steel-making industry due to their unique properties and performance advantages. Their ability to efficiently conduct electricity and withstand high temperatures positions them as a vital component in the electric arc furnace process. As the metallurgical sector continues to evolve, ongoing developments in graphite electrode technology will likely enhance their effectiveness and sustainability, ensuring their pivotal role in future steel production. Understanding these aspects is crucial for industry professionals looking to optimize their operations and meet the demands of modern steel manufacturing.
One of the primary advantages of graphite electrodes is their high thermal and electrical conductivity. This allows them to effectively transfer electrical energy to the charge in the furnace, facilitating efficient melting. Additionally, graphite has a high melting point, which enables it to withstand the intense heat generated during the steel-making process without degrading. This durability results in longer operational life and reduced frequency of electrode replacement, making the overall process more cost-effective.
Moreover, the purity and quality of the graphite used in the production of these electrodes are crucial. High-quality graphite electrodes are made from premium petroleum coke and are often baked and graphitized at high temperatures to enhance their properties. This ensures that the electrodes maintain their performance under the extreme conditions of an electric arc furnace. When selecting graphite electrodes for steel making, it is essential to consider factors such as the electrode diameter, length, and density, as these characteristics significantly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of the steel-making process.
Additionally, the use of graphite electrodes has evolved with advancements in technology. Innovations such as the use of ultra-high-power (UHP) graphite electrodes allow for higher current densities and improved melting capabilities, which is particularly beneficial in operations aiming for higher production rates. Furthermore, as the industry moves toward sustainability, research is being conducted to improve the recycling and reusability of graphite electrodes, thus minimizing waste.
In conclusion, graphite electrodes are indispensable in the steel-making industry due to their unique properties and performance advantages. Their ability to efficiently conduct electricity and withstand high temperatures positions them as a vital component in the electric arc furnace process. As the metallurgical sector continues to evolve, ongoing developments in graphite electrode technology will likely enhance their effectiveness and sustainability, ensuring their pivotal role in future steel production. Understanding these aspects is crucial for industry professionals looking to optimize their operations and meet the demands of modern steel manufacturing.
Focus On Hot Spots
RP Graphite Electrodes: Transforming Conductivity in Metallurgical Processes
RP Graphite Electrodes: Enhancing Conductivity in Metallurgical Applications
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to RP Graphite Electrodes
2. Understanding Graphite and Its Properties
3. The Role of RP Graphite Electrodes in Metallurgy
4. Benefits of Using RP Graphite Electrodes
5. The Manufacturing Process of RP Graphite Electrodes
6. Applications of RP Graphite Electrodes
The Essential Guide to Graphite Blocks in Metallurgy and Energy Industries
Graphite blocks are pivotal materials in the metallurgy and energy industries, particularly within the non-metallic mineral products sector. These blocks, made from natural or synthetic graphite, possess unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. One of the most notable characteristics of graphite is its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. This property









