Understanding Graphite Electrodes: Key Components in Steel Making
Summary:
Graphite electrodes for steel making are indispensable in the production of high-quality steel through electric arc furnaces (EAFs). These electrodes are used to conduct electricity and generate the high temperatures needed to melt scrap steel and other raw materials. As the demand for steel continues to rise globally, understanding the features and benefits of graphite electrodes becomes increasi
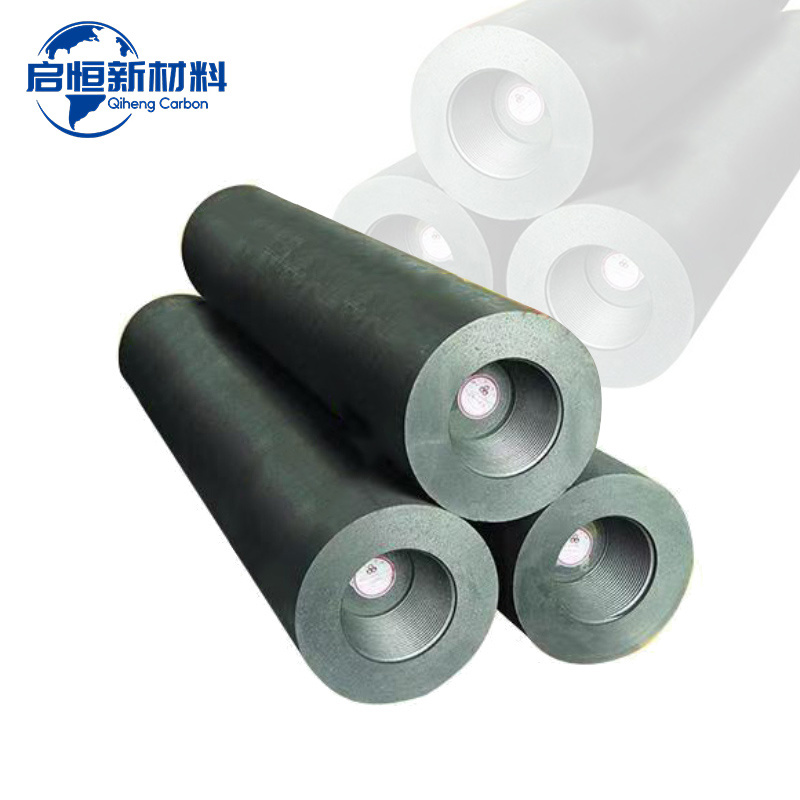
Graphite electrodes for steel making are indispensable in the production of high-quality steel through electric arc furnaces (EAFs). These electrodes are used to conduct electricity and generate the high temperatures needed to melt scrap steel and other raw materials. As the demand for steel continues to rise globally, understanding the features and benefits of graphite electrodes becomes increasingly important for metallurgical operations.
One of the primary reasons graphite electrodes are favored in steel production is their exceptional conductivity. Graphite is an excellent conductor of electricity, which allows for efficient energy transfer during the steel-making process. This efficiency not only reduces overall energy consumption but also contributes to lower operational costs, making it a preferred material in the industry.
The production of graphite electrodes involves several key steps. Initially, petroleum coke and coal tar pitch are blended and heated to form a carbonaceous material. This material is then shaped into the desired electrode form. After shaping, the electrodes undergo a baking process, where they are heated at high temperatures in a controlled environment, transforming them into a solid carbon structure. The final step involves graphitization, which imparts enhanced electrical conductivity and thermal resistance, ensuring optimal performance in demanding steel-making conditions.
In addition to their electrical properties, graphite electrodes exhibit excellent thermal stability and resistance to oxidation. This enables them to withstand the high temperatures encountered in electric arc furnaces, where temperatures can exceed 3,000 degrees Celsius. Moreover, the ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions is critical for ensuring consistent steel quality and operational efficiency.
Graphite electrodes come in various sizes and grades to suit specific applications and requirements in the steel-making process. Factors such as electrode diameter, length, and grade quality can significantly influence melting efficiency and electrode lifespan. Choosing the right type of graphite electrode is essential for achieving optimal performance and minimizing downtime during production.
As the steel industry continues to evolve, innovations in graphite electrode technology are also emerging. Manufacturers are exploring advanced materials and production techniques to enhance the performance and sustainability of these electrodes. This includes the development of eco-friendly alternatives and optimizing designs to reduce material waste.
In summary, graphite electrodes for steel making are fundamental components that facilitate efficient energy transfer and high-temperature processes in electric arc furnaces. Understanding their properties, production methods, and applications can empower businesses to make informed decisions that improve their steel production practices. As the industry continues to advance, staying abreast of developments in graphite electrode technology will be key to maintaining a competitive edge in the metallurgical landscape.
One of the primary reasons graphite electrodes are favored in steel production is their exceptional conductivity. Graphite is an excellent conductor of electricity, which allows for efficient energy transfer during the steel-making process. This efficiency not only reduces overall energy consumption but also contributes to lower operational costs, making it a preferred material in the industry.
The production of graphite electrodes involves several key steps. Initially, petroleum coke and coal tar pitch are blended and heated to form a carbonaceous material. This material is then shaped into the desired electrode form. After shaping, the electrodes undergo a baking process, where they are heated at high temperatures in a controlled environment, transforming them into a solid carbon structure. The final step involves graphitization, which imparts enhanced electrical conductivity and thermal resistance, ensuring optimal performance in demanding steel-making conditions.
In addition to their electrical properties, graphite electrodes exhibit excellent thermal stability and resistance to oxidation. This enables them to withstand the high temperatures encountered in electric arc furnaces, where temperatures can exceed 3,000 degrees Celsius. Moreover, the ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions is critical for ensuring consistent steel quality and operational efficiency.
Graphite electrodes come in various sizes and grades to suit specific applications and requirements in the steel-making process. Factors such as electrode diameter, length, and grade quality can significantly influence melting efficiency and electrode lifespan. Choosing the right type of graphite electrode is essential for achieving optimal performance and minimizing downtime during production.
As the steel industry continues to evolve, innovations in graphite electrode technology are also emerging. Manufacturers are exploring advanced materials and production techniques to enhance the performance and sustainability of these electrodes. This includes the development of eco-friendly alternatives and optimizing designs to reduce material waste.
In summary, graphite electrodes for steel making are fundamental components that facilitate efficient energy transfer and high-temperature processes in electric arc furnaces. Understanding their properties, production methods, and applications can empower businesses to make informed decisions that improve their steel production practices. As the industry continues to advance, staying abreast of developments in graphite electrode technology will be key to maintaining a competitive edge in the metallurgical landscape.
Previous:
Focus On Hot Spots
RP Graphite Electrodes: Transforming Conductivity in Metallurgical Processes
RP Graphite Electrodes: Enhancing Conductivity in Metallurgical Applications
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to RP Graphite Electrodes
2. Understanding Graphite and Its Properties
3. The Role of RP Graphite Electrodes in Metallurgy
4. Benefits of Using RP Graphite Electrodes
5. The Manufacturing Process of RP Graphite Electrodes
6. Applications of RP Graphite Electrodes
The Essential Guide to Graphite Blocks in Metallurgy and Energy Industries
Graphite blocks are pivotal materials in the metallurgy and energy industries, particularly within the non-metallic mineral products sector. These blocks, made from natural or synthetic graphite, possess unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. One of the most notable characteristics of graphite is its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. This property









