UHP Graphite Electrodes: Unveiling Their Significance in Electric Arc Furnaces
Summary:
UHP Graphite Electrodes: Unveiling Their Significance in Electric Arc Furnaces
Table of Contents
Introduction to UHP Graphite Electrodes
What are UHP Graphite Electrodes?
Manufacturing Process of UHP Graphite Electrodes
The Role of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Electric Arc Furnaces
Benefits of Using UHP Graphite Electrodes
Challenges and Limitations of UHP Graphite Electrodes
Future T
UHP Graphite Electrodes: Unveiling Their Significance in Electric Arc Furnaces
Table of Contents
- Introduction to UHP Graphite Electrodes
- What are UHP Graphite Electrodes?
- Manufacturing Process of UHP Graphite Electrodes
- The Role of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Electric Arc Furnaces
- Benefits of Using UHP Graphite Electrodes
- Challenges and Limitations of UHP Graphite Electrodes
- Future Trends in UHP Graphite Electrodes
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to UHP Graphite Electrodes
In the realm of metallurgy, particularly in steel production, **Ultra-High Power (UHP) Graphite Electrodes** play an indispensable role. As a critical component in **Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs)**, these electrodes facilitate the melting of scrap steel and other materials, making them vital for modern steelmaking. Understanding the intricacies of UHP graphite electrodes not only enhances our appreciation of their significance but also sheds light on the future of steel production.
What are UHP Graphite Electrodes?
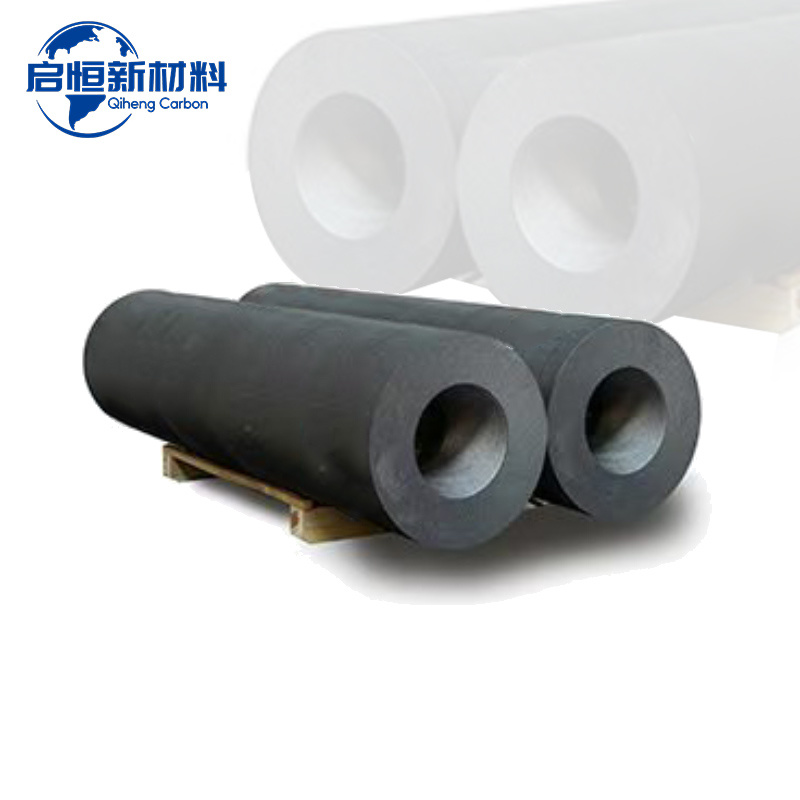
UHP graphite electrodes are specialized conductive rods made primarily of graphite that can withstand extremely high temperatures and carry electric current efficiently. These electrodes are categorized based on their power ratings: UHP, HP (High Power), and RP (Regular Power). UHP electrodes are engineered for higher current carrying capacities and are utilized in applications demanding superior performance, such as in Electric Arc Furnaces.
Composition and Properties
The primary component of UHP graphite electrodes is **petroleum needle coke**, which is known for its high carbon content and low impurity levels. Once processed, the electrodes exhibit remarkable properties:
- **High conductivity**: Essential for efficient electric current transfer.
- **Thermal stability**: Maintains structural integrity at elevated temperatures.
- **Low expansion coefficient**: Minimizes dimensional changes under temperature fluctuations.
Manufacturing Process of UHP Graphite Electrodes
The production of UHP graphite electrodes involves several meticulous steps that ensure high quality and performance.
1. Raw Material Selection
The manufacturing journey begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, primarily petroleum needle coke. The quality of the coke significantly affects the electrode's performance.
2. Calcination
The selected needle coke undergoes calcination at high temperatures to remove volatile impurities, enhancing its carbon content and structural integrity.
3. Mixing and Forming
The calcined coke is mixed with a binding agent, typically pitch, to form a paste. This paste is then shaped into electrode blocks through a pressing process.
4. Baking
These shaped blocks are baked in a controlled environment at high temperatures, a process that carbonizes the pitch, providing strength to the electrodes.
5. Graphitization
The baked electrodes are then subjected to graphitization, a heat treatment process that transforms the carbon structure into graphite, enhancing electrical conductivity.
6. Machining and Quality Control
Finally, the electrodes are machined to precise dimensions and undergo rigorous quality control tests to ensure they meet industry standards.
The Role of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Electric Arc Furnaces
UHP graphite electrodes serve as the primary conduits for electric current in Electric Arc Furnaces. The high temperatures achieved in EAFs facilitate the melting and refining of scrap steel, and the efficiency of this process hinges on the performance of the electrodes.
1. Current Conduction
When electric current is passed through the electrodes, it creates an electric arc between the electrodes and the scrap material, generating sufficient heat to melt the scrap.
2. Temperature Control
The ability to maintain temperature control is crucial in EAF operations. UHP electrodes provide the necessary thermal stability to manage the melting process effectively.
3. Environmental Impact
The use of UHP graphite electrodes in EAFs contributes to more environmentally friendly steel production methods, as they allow for higher recycling rates of scrap steel, reducing the reliance on raw materials.
Benefits of Using UHP Graphite Electrodes
The adoption of UHP graphite electrodes brings several benefits to the steelmaking process:
1. Enhanced Efficiency
UHP graphite electrodes improve energy efficiency in Electric Arc Furnaces, leading to reduced operational costs and increased productivity.
2. Superior Performance
With their ability to handle high current loads, UHP electrodes offer superior performance compared to their counterparts, making them ideal for demanding applications.
3. Longer Lifespan
The durability and low wear rates of UHP electrodes contribute to a longer lifespan, minimizing the frequency of replacements and enhancing cost-effectiveness.
Challenges and Limitations of UHP Graphite Electrodes
Despite their advantages, UHP graphite electrodes do face several challenges:
1. Cost Implications
The production of UHP graphite electrodes involves significant investment in raw materials and manufacturing processes, which can make them costly compared to lower-rated electrodes.
2. Environmental Considerations
The production process for UHP electrodes can have environmental implications, particularly concerning the carbon footprint and resource consumption.
3. Market Volatility
The prices of raw materials, particularly petroleum needle coke, can be volatile, impacting the overall production costs for manufacturers of UHP graphite electrodes.
Future Trends in UHP Graphite Electrodes
As the steel industry continues to evolve, so too will the technologies surrounding UHP graphite electrodes:
1. Advancements in Materials
Research is ongoing into alternative materials and composites that can enhance the performance and reduce the costs of UHP graphite electrodes.
2. Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The adoption of automation and smart manufacturing technologies in the production process will likely lead to increased efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
3. Sustainability Practices
There is a growing emphasis on sustainability in the steel industry. Future developments may focus on minimizing the environmental footprint of UHP graphite electrode production and recycling more materials.
Conclusion
UHP graphite electrodes are undeniably vital to the function and efficacy of Electric Arc Furnaces in the steelmaking industry. Their high conductivity, durability, and efficiency make them essential for modern steel production. While challenges exist, ongoing research and advancements promise a bright future for UHP graphite electrodes, ensuring they remain at the forefront of metallurgical technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between UHP and HP graphite electrodes?
UHP graphite electrodes are designed for higher current loads compared to HP electrodes, making them suitable for more demanding applications.
2. How are UHP graphite electrodes manufactured?
The manufacturing process involves several steps, including raw material selection, calcination, mixing, baking, graphitization, and quality control.
3. What are the primary applications of UHP graphite electrodes?
UHP graphite electrodes are primarily used in Electric Arc Furnaces for melting scrap steel and other metallurgical processes.
4. Are there any environmental concerns associated with UHP graphite electrodes?
Yes, the production process can impact the environment, particularly concerning carbon emissions and resource consumption.
5. What is the expected future of UHP graphite electrodes in the industry?
The future includes advancements in material technology, greater automation in manufacturing, and a focus on sustainability practices.
Focus On Hot Spots
RP Graphite Electrodes: Transforming Conductivity in Metallurgical Processes
RP Graphite Electrodes: Enhancing Conductivity in Metallurgical Applications
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to RP Graphite Electrodes
2. Understanding Graphite and Its Properties
3. The Role of RP Graphite Electrodes in Metallurgy
4. Benefits of Using RP Graphite Electrodes
5. The Manufacturing Process of RP Graphite Electrodes
6. Applications of RP Graphite Electrodes
The Essential Guide to Graphite Blocks in Metallurgy and Energy Industries
Graphite blocks are pivotal materials in the metallurgy and energy industries, particularly within the non-metallic mineral products sector. These blocks, made from natural or synthetic graphite, possess unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. One of the most notable characteristics of graphite is its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. This property









