Understanding the Lifecycle of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Industrial Use
Summary:
Understanding the Lifecycle of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Industrial Use
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to UHP Graphite Electrodes
2. What Are UHP Graphite Electrodes?
3. Manufacturing Process of UHP Graphite Electrodes
4. Applications of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Various Industries
5. Advantages of Using UHP Graphite Electrodes
6. Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
7. Mai
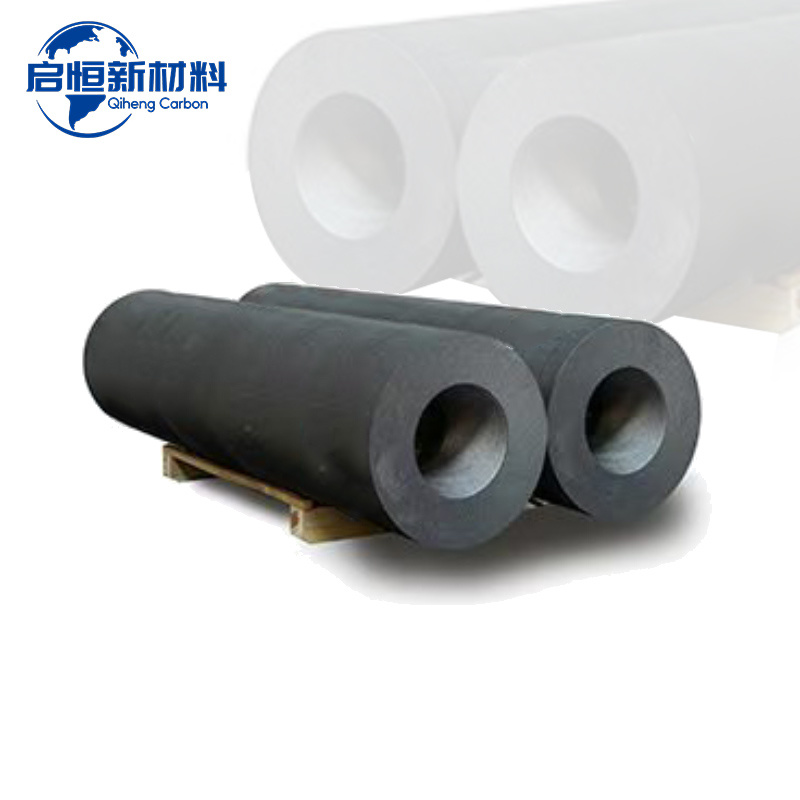
Understanding the Lifecycle of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Industrial Use
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to UHP Graphite Electrodes
- 2. What Are UHP Graphite Electrodes?
- 3. Manufacturing Process of UHP Graphite Electrodes
- 4. Applications of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Various Industries
- 5. Advantages of Using UHP Graphite Electrodes
- 6. Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
- 7. Maintenance Practices for Extending Lifespan
- 8. Future Trends in UHP Graphite Electrodes
- 9. Conclusion
- 10. FAQs
1. Introduction to UHP Graphite Electrodes
UHP (Ultra High Power) graphite electrodes are essential components in the steelmaking process and other industrial applications. These electrodes facilitate the electric arc furnace (EAF) process, enabling the production of high-quality steel and other metals. The demand for UHP graphite electrodes has surged as industries strive for improved efficiency and sustainability. This article will explore the lifecycle of UHP graphite electrodes, detailing their manufacturing, applications, advantages, and future trends while focusing on sustainable practices.
2. What Are UHP Graphite Electrodes?
UHP graphite electrodes are composed of high-purity graphite, designed to withstand the extreme temperatures generated during the steelmaking process. These electrodes differ from regular graphite electrodes in that they can handle higher current loads, making them suitable for modern electric arc furnaces. Their unique properties—such as high thermal conductivity, low electrical resistance, and resistance to thermal shock—make them indispensable in the metallurgical industry.
2.1 Composition of UHP Graphite Electrodes
The primary material used in UHP graphite electrodes is petroleum needle coke, which is combined with pitch to improve its mechanical strength. This composition allows UHP electrodes to achieve superior performance and longevity in extreme conditions.
3. Manufacturing Process of UHP Graphite Electrodes
The manufacturing process of UHP graphite electrodes is intricate and consists of several stages, including:
3.1 Raw Material Selection
The first step involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, primarily needle coke, which is crucial for producing electrodes with superior properties.
3.2 Calcination
The raw materials are subjected to high temperatures in a calciner, where they undergo thermal treatment to eliminate volatile components and enhance carbon content.
3.3 Mixing and Grinding
Following calcination, the calcined coke is mixed with a liquid binder (pitch) and ground to a fine powder, ensuring uniformity.
3.4 Forming
The mixture is then shaped into cylindrical forms through a process known as extrusion or molding.
3.5 Baking
The formed electrodes are baked in ovens at high temperatures to convert the binder into a solid carbon matrix, enhancing strength and integrity.
3.6 Graphitization
In this crucial step, the baked electrodes are subjected to even higher temperatures (around 3000°C) in an inert atmosphere, transforming the carbon structure into a graphitic form.
3.7 Machining and Quality Control
Finally, the electrodes are machined to achieve precise dimensions and subjected to rigorous quality control tests to ensure they meet industry standards.
4. Applications of UHP Graphite Electrodes in Various Industries
UHP graphite electrodes are utilized across multiple sectors due to their unique properties. Some of the primary applications include:
4.1 Steelmaking
The most significant use of UHP graphite electrodes is in electric arc furnaces for steel production, where they enable melting and refining processes.
4.2 Foundry Operations
In foundries, these electrodes facilitate the melting of non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum and copper, enhancing overall efficiency.
4.3 Manufacturing of Silicon
UHP graphite electrodes are also critical in producing silicon metal, used extensively in the electronics and solar industries.
4.4 Production of Other Alloys
Beyond steel and silicon, UHP electrodes aid in producing various metal alloys, ensuring the desired properties in the final products.
5. Advantages of Using UHP Graphite Electrodes
The benefits of utilizing UHP graphite electrodes in industrial applications are numerous:
5.1 High Conductivity
The excellent electrical conductivity of UHP electrodes allows for efficient energy use during operations, leading to reduced production costs.
5.2 Superior Thermal Stability
UHP graphite electrodes exhibit remarkable thermal stability, enabling them to operate at high temperatures without degradation.
5.3 Extended Lifespan
These electrodes last longer than traditional graphite electrodes, resulting in fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs.
5.4 Environmental Benefits
Using UHP graphite electrodes promotes cleaner production methods, as they contribute to higher recycling rates and lower emissions.
6. Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
As industries become increasingly aware of their environmental footprint, understanding the sustainability of UHP graphite electrodes is essential. The production process can be energy-intensive, but advancements in technology are helping mitigate this impact.
6.1 Recycling Initiatives
Recycling UHP graphite electrodes after their lifespan can significantly reduce waste and lower the demand for new raw materials, promoting a circular economy.
6.2 Carbon Footprint Reduction
Innovative production techniques aim to lower the carbon footprint associated with graphite electrode manufacturing, enhancing overall sustainability.
7. Maintenance Practices for Extending Lifespan
To maximize the lifespan and efficiency of UHP graphite electrodes, proper maintenance practices are crucial:
7.1 Regular Inspections
Conducting regular inspections can identify wear and tear, allowing for timely replacements and avoiding production downtime.
7.2 Proper Handling Techniques
Implementing best practices in handling and installation minimizes the risk of damage during transportation and setup.
7.3 Optimizing Operating Conditions
Maintaining optimal conditions in the electric arc furnace can significantly enhance electrode performance and longevity.
8. Future Trends in UHP Graphite Electrodes
The future of UHP graphite electrodes is closely linked to advancements in technology and changing industry demands:
8.1 Development of New Materials
Research into alternative materials may yield products with even better performance and lower environmental impact.
8.2 Automation in Manufacturing
Increased automation and AI integration in the manufacturing process can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality control.
8.3 Focus on Sustainability
As sustainability continues to be a priority, the development of eco-friendly production methods and recycling initiatives will shape the future of UHP graphite electrodes.
9. Conclusion
Understanding the lifecycle of UHP graphite electrodes is crucial for industries that rely on high-performance materials for their operations. From the meticulous manufacturing process to the various applications and sustainability considerations, UHP graphite electrodes play an integral role in modern industrial practices. By embracing innovative practices and maintaining a focus on sustainability, industries can maximize the benefits of these essential components, ensuring a more efficient and environmentally friendly future.
10. FAQs
10.1 What distinguishes UHP graphite electrodes from regular graphite electrodes?
UHP graphite electrodes can handle higher current loads and temperatures, making them suitable for advanced electric arc furnaces.
10.2 What are the main applications of UHP graphite electrodes?
They are primarily used in steelmaking, foundries, and silicon production, among other industrial applications.
10.3 How can the lifespan of UHP graphite electrodes be extended?
Regular inspections, proper handling, and optimizing operating conditions can significantly extend their lifespan.
10.4 What is the environmental impact of UHP graphite electrode manufacturing?
While manufacturing can be energy-intensive, advancements in technology and recycling initiatives aim to reduce environmental impacts.
10.5 What future trends are expected in UHP graphite electrodes?
Expect to see innovations in materials, increased automation, and a greater focus on sustainability shaping the future of UHP graphite electrodes.
Focus On Hot Spots
RP Graphite Electrodes: Transforming Conductivity in Metallurgical Processes
RP Graphite Electrodes: Enhancing Conductivity in Metallurgical Applications
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to RP Graphite Electrodes
2. Understanding Graphite and Its Properties
3. The Role of RP Graphite Electrodes in Metallurgy
4. Benefits of Using RP Graphite Electrodes
5. The Manufacturing Process of RP Graphite Electrodes
6. Applications of RP Graphite Electrodes
The Essential Guide to Graphite Blocks in Metallurgy and Energy Industries
Graphite blocks are pivotal materials in the metallurgy and energy industries, particularly within the non-metallic mineral products sector. These blocks, made from natural or synthetic graphite, possess unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. One of the most notable characteristics of graphite is its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. This property









